“Multimodel estimates of intercontinental source-receptor relationships for ozone pollution” https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2008JD010816
This work evaluates the contribution of foreign emission on local ozone pollution for East Asia, Europe, North America and South Asia.
The evaluation is performed by a 21 CTM sensitivity test. Emissions are reduced by 20% for EA, EU, NA, SA individually, and the surface ozone change at each region in response to emission change from foreign vs domestic region.
Emissions to be reduced 20% includes anthropogenic emissions of the O3 precursors, NOx, NMVOC, and CO (individually and combined).
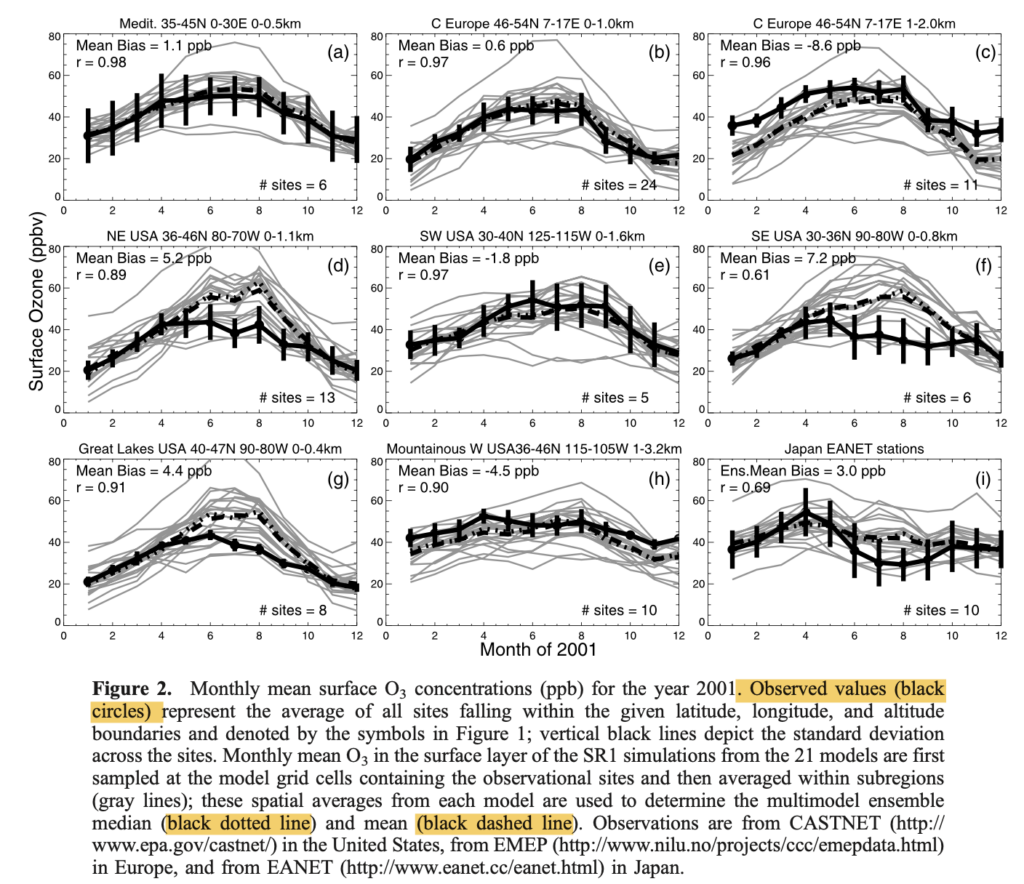
For the base case, model ensemble mean surface ozone largely reproduce observation over EU, but overestimates >10ppb in eastern US and Japan.
Sum of ozone change responses to NOx + CO + NMVOCs ~= ozone change response to all precursors.
Domestic emission is more important than foreign emission on local severe ozone pollution.
1996-2002, the estimated North Hemisphere increase in background surface ozone is ~0.1ppb/year.
Ozone change response to reduction of 20% of global atmospheric methane ~= sum of ozone change responses to NOx+NMVOC+CO from foreign sources.
Leave a Reply